Diagnostic Procedures
Overview of Pediatric Cardiology
At Bengal Child Heart Group, we offer a comprehensive range of treatments for various pediatric heart conditions, ensuring each child receives personalized and expert care. Our experienced team of pediatric cardiologists is dedicated to diagnosing, treating, and managing heart diseases in children from birth through adolescence.
Echocardiography (TTE/TEE/Fetal):
- Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): A non-invasive ultrasound test that provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. This is the most common type of echocardiogram performed on children.
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): Involves inserting a probe with an ultrasound transducer into the esophagus to obtain clearer images of the heart, especially useful for complex heart conditions.
- Fetal Echocardiography: Conducted during pregnancy to assess the heart of the unborn child, helping in early detection of congenital heart defects.
Electrocardiogram (ECG):
- A non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart to detect arrhythmias, heart blockages, and other cardiac abnormalities. It is quick and painless, providing essential information about the heart’s rhythm and electrical activity.

Holter Monitoring:
- Continuous 24-48 hour ECG monitoring to identify intermittent arrhythmias and other cardiac issues that may not be captured during a standard ECG. Patients wear a portable device that records heart activity as they go about their daily activities.

Cardiac MRI and CT Scans:
- Cardiac MRI: Provides detailed images of the heart and blood vessels using magnetic resonance imaging. It helps in evaluating heart structure, function, and blood flow without radiation exposure.
- Cardiac CT Scan: Uses computed tomography to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the heart, useful in diagnosing complex congenital heart defects and assessing coronary arteries.
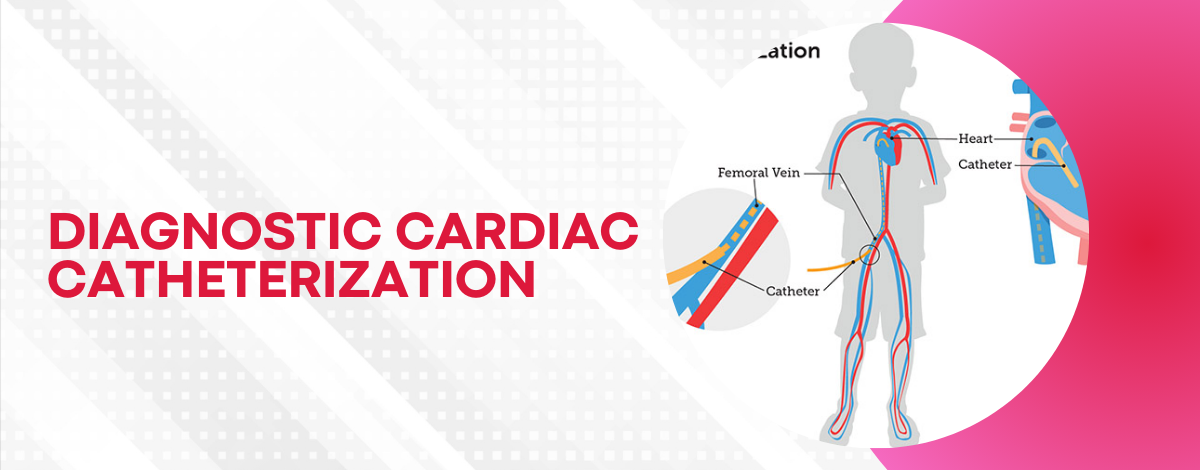
Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization:
- An invasive procedure where a thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. It allows for direct measurement of heart pressures, oxygen levels, and detailed imaging of heart structures. This procedure is crucial for diagnosing complex heart conditions and planning appropriate interventions.

